ESD Equipment Explained: How to Set Up an ESD Workstation
In this article we explain how anti-static equipment including mats and wrist straps work and how to set up correctly an ESD workstation that is safe for handling components that are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD).
What is Static Electricity?
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges on material. The charge is static, in contrast to current electricity which flows through conductors such as wiring in a circuit. Static electricity can build up easily when insulators, materials that have a high resistance to electric current and don’t conduct electricity well, come into contact with each other.
We experience static charges and discharges every day. You may be familiar with getting a static shock when touching a door handle or even another person. This shock is the result of the static electricity rapidly discharging, resulting in a neutralisation of charge.
Useful Applications of Static Electricity
Static electricity can be very useful and is used in flash photography, photocopiers, printers, air filters and more. However, in some instances, static electricity can be problematic in some situations.
Handling sensitive electronic components
Some electronic components are very sensitive to static and the sudden discharge of electricity from your body to the component, which is harmless to humans, can cause irreparable damage to the components or devices.
Antistatic Devices Explained
Anti-static devices help minimise the risk of damage caused by static by inhibiting the build-up of static electricity. This prevents the chance of a sudden discharge of electricity via the sensitive component, therefore protecting it from damage.
Antistatic Bag
An antistatic bag is used to store electronic components which are sensitive to static electricity. Conductive antistatic bags contain a layer of conductive metal, which forms a non-conductive barrier and a shield which protects the contents from the static charge using the Faraday cage effect.
Antistatic Bar
An antistatic bar removes static electricity from a production line, preventing issues including dust clinging to products, products clinging to themselves, rollers, machine beds or frames as well as materials jamming or tearing.
Antistatic Clothing
Antistatic clothing contains conductive threads, creating a wearable Faraday cage. Most antistatic garments need to be grounded, i.e. connected to the ground with a strap.
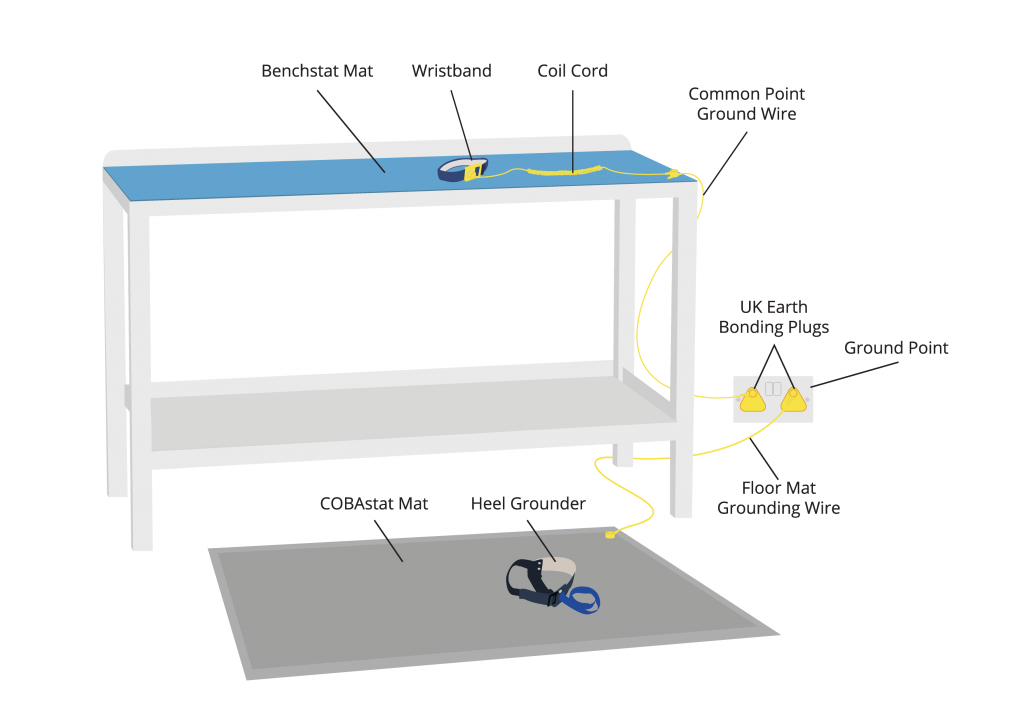
Antistatic Mat
An antistatic mat or ground mat allows electrostatic discharge to flow across the surface slowly, in a controlled manner, thus preventing the rapid discharge which can damage sensitive components. The mat is grounded by being connected to the mains plug outlet via an earth bonding plug. Both antistatic bench and floor mats are available for working with electronic components.
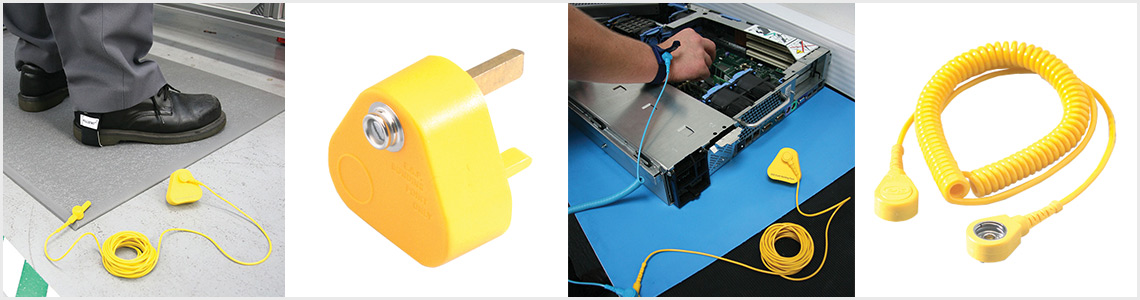
Antistatic Wrist Strap
An antistatic wrist strap or ESD wristband is used to ground a person who works on sensitive electronic components. It is worn around the wrist and connected to the mains plug outlet via an earth bonding plug.
Antistatic Matting at CSI Products
At CSI Products, we provide a range of equipment suitable for working with components that are sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Our range of COBAstat and Senso Dial mats are reliable static-dissipative ESD approved floor mats. These durable floor mats protect operatives and equipment from static build-up. In addition, they provide an anti-fatigue surface for improved comfort when standing for extended periods of time.
HR and Benchstat are work surface mats. They are static dissipative, with a conductive buried layer to help protect components. Both work surface mats meet or exceed IEC51349-5-1 resistance requirements. The matting kits include a work surface mat, a common point grounding wire to ground the mat, an ESD wristband, a coil cord to ground the wristband and a UK earth bonding plug to connect lead to earth.
How to Set Up an ESD Workstation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Work surface mat and wrist strap
 |
1. Lay the work surface mat flat on the workbench with the connector facing toward the operative. |
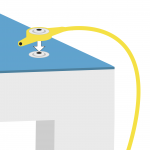 |
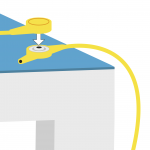
2. Connect the common point grounding wire to the stud on the mat. |
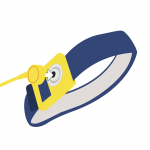 |
3. Connect the wristband to the coil cord. |
 |
4. Connect the coil cord to the common point grounding wire. |
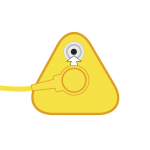 |
5. Connect the common point grounding wire to the earth bonding plug which has a metal earth pin and plastic neutral and mains voltage pins. |
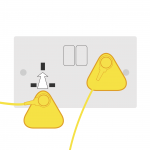 |
6. Plug the earth bonding plug into your UK standard plug outlet. |
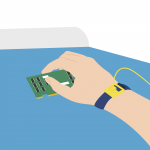 |
7. Wear the wristband. |
Floor mat
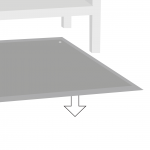 |
1. Lay the floor mat flat on the floor with the connector facing toward the workbench. |
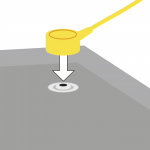 |
2. Connect the floor mat grounding wire to the floor mat. |
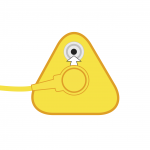 |
3. Connect the floor mat grounding wire to an earth bonding plug. |
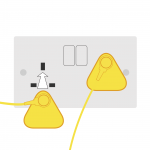 |
4. Plug the earth bonding plug into your UK standard plug outlet. |
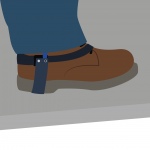 |
5. Use heel grounders on both feet to ensure you are grounded when standing on an ESD floor mat. The heel grounders tuck into your shoe and ensure a continuous connection from your skin to the floor mat. |
Explore the Full Range of ESD Equipment
You can browse our full range of ESD equipment and matting here.
Get in Touch
If you have any questions or would like more information, please contact our expert product advisors on 08082397985 or [email protected].


